大气潮汐波是中高层大气中非常重要的一类大尺度强烈波动现象。大气潮汐波的振幅在中间层低热层(mesosphere and lower thermosphere, mlt)区域很大,从而严重影响该区域的动力学、光化学、辐射、以及能量收支与转换,并且可以进一步引起热层和电离层中多种参数和物理过程的变化。
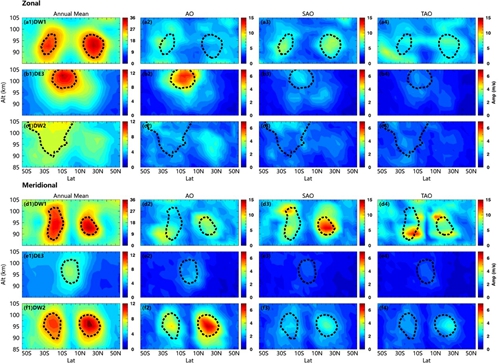
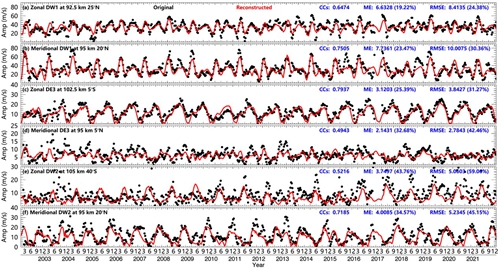
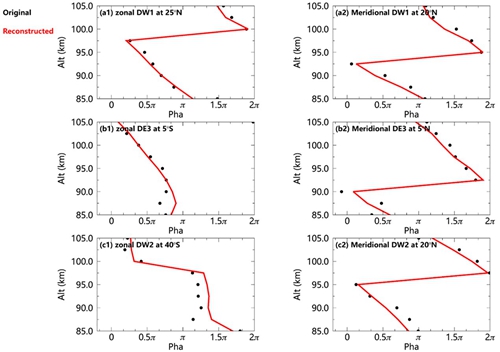
目前,对全球范围内潮汐风场的各个分量的季节变化和年际变化缺乏系统的研究。同时潮汐波的参数化对于全球大气模式的构建非常重要。中国科学院国家空间科学中心空间天气学国家重点实验室中高层大气研究团队徐寄遥研究员和博士生刘阳坤等人利用timed 卫星上搭载的设备tidi (timed doppler interferometer)观测的20年的全球中性水平风场数据,对低热层区域(85km-105km)的全球潮汐风场(周日潮汐、半日潮汐、8小时潮汐)的季节变化及其对平流层准两年振荡和太阳活动周期的响应进行了系统性研究。为避免磁暴的干扰,我们选取地磁平静期(kp≤3)的观测数据。研究发现,潮汐风场在其振幅最大的区域均表现出显著的季节变化和年际变化,如图1所示,迁移潮汐分量不仅表现出显著的年变化(ao)和半年变化(sao),同时研究发现迁移潮汐分量还表现出显著的三分之一年变化(tao),而非迁移潮汐分量则没有表现出显著的三分之一年变化。另外,该研究表明潮汐风场的季节变化对平流层准两年振荡和太阳活动周期具有显著的不可忽略的响应。最后,该研究给出了潮汐风场的振幅和相位随时间变化的参数化经验公式,如图2和图3所示,该经验公式能较好地描述各个潮汐分量的振幅随时间的变化的特征和相位随高度的变化特征。
该项研究形成的系列研究成果发表在国际期刊journal of geophysical research-space physics上。相关经验公式和数据存放在国家空间科学数据中心,方便广大同行使用。
论文链接如下:
liu, y., xu, j., smith, a. k., & liu, x. (2024a). seasonal and interannual variations of global tides in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere neutral winds: i. diurnal tides. journal of geophysical research: space physics, 129, e2023ja031887. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023ja031887
liu, y., xu, j., smith, a. k., & liu, x. (2024b). seasonal and interannual variations of global tides in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere neutral winds: ii. semidiurnal and terdiurnal tides. journal of geophysical research: space physics, 129, e2023ja031846. https://doi.org/10.1029/2023ja031846
周日潮汐、半日潮汐和8小时潮汐的经验公式的idl代码和数据集链接如下:
liu, y., xu, j., smith, a. k., & liu, x. (2023a). empirical formulas for temporal variations of amplitudes of diurnal tides in horizontal wind in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. (version v2) [dataset]. science data bank. https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.o00009.00227
liu, y., xu, j., smith, a. k., & liu, x. (2023b). empirical formulas for temporal variations of amplitudes of semidiurnal tides in horizontal wind in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. (version v2) [dataset]. science data bank. https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.o00009.00229
liu, y., xu, j., smith, a. k., & liu, x. (2023c). empirical formulas for temporal variations of amplitudes of terdiurnal tides in horizontal wind in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. (version v2) [dataset]. science data bank. https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.o00009.00230
图1 在纬向风(a-c)和经向风(d-f)中,周日潮汐分量(dw1:a和d;de3:b和e;dw2:c和f)的年平均振幅(第一列)、年变化振幅(第二列)、半年变化振幅(第三列)和三分之一年变化振幅(第四列)的20年平均纬度-高度分布。峰值区域用黑色虚线圈出
图2 纬向dw1(a)、经向dw1(b)、纬向de3(c)、经向de3(d)、纬向dw2(e)和经向dw2(f)在其峰值纬度和高度(纬度和高度标记在图中)的原始(黑点)和重构(红线)振幅。相关系数(ccs)、平均误差(me)和均方根误差(rmse)标记在图中。me和rmse与其潮汐分量的平均振幅的比例标注在括号中
图3 dw1(纬向:a1;经向:a2)、de3(纬向:b1;经向:b2)、dw2(纬向:c1;经向:c2)的原始相位(黑点)和重构相位(红线)在其峰值纬度和季节的垂直剖面
(供稿:天气室)